Can AI Truly Be Fair? A Framework for Ethical AI Use in Hiring
Did you know that artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping how companies hire? About 99% of hiring managers say they use some form of AI in their hiring process, and 95% say they plan to invest in it.
From using Generative AI (genAI) for creating job postings to applying Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for sorting and screening applications, AI is everywhere. Conversational AI is conducting virtual job interviews, while Machine Learning (ML) is helping assess candidates. But with all these innovations comes a pressing question: Can AI truly be fair?
This blog provides a framework for using AI ethically in the hiring process. Read on to find out what fairness looks like and how to build it into your recruitment strategy.
The Use of AI in Hiring
AI is human intelligence simulated in technological form. It enables computer systems and digital tools to process information and perform tasks that typically require human input, or that are very helpful for teams when hiring specific professionals like virtual legal assistants.
You’ve likely encountered AI in everyday tools, using genAI like ChatGPT to generate content pieces, conversational AI like Chatbots to interact with web users, and voice assistants like Siri or Alexa responding to verbal commands. These are just a few of the most recognizable forms of AI in action, powered by innovative AI Development services!
In recruitment, AI is reshaping how organizations find and evaluate talent. So, what technologies are driving this change?
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): It involves using automated software to handle routine hiring tasks, such as logging new job applications, verifying test scores, and organizing candidates’ data. The core purpose is to streamline HR functions and improve efficiency, freeing up the HR team from tedious manual tasks, allowing them to hire more quickly and efficiently!
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms can analyze past recruitment data to make hiring predictions and decisions. This can include screening job applications based on preset criteria, such as work experience, educational background (courses taken), or skill sets (specific hard and soft skills needed) aligned with the role.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables computer systems and digital tools to process and interact with human language data. They can read text, listen to speech, understand context, and even generate human-like responses. They’re typically used in the online screening process, whether to assist with assessments or conduct virtual interviews.
- Computer Vision: It empowers computer systems and software apps to see and interpret visual data from images or videos, while leveraging image optimization techniques to enhance clarity, accuracy, and performance. This includes recognizing objects and movements. In the context of hiring, it paves the way for AI-human interactions, allowing the system to monitor candidate actions that may be considered unfair. A dedicated development team can build and fine-tune such AI-driven solutions, ensuring objectivity and fairness during online assessments or virtual interviews.
- Speech Recognition: This tech enables digital tools to accurately understand and interpret verbal human language. In modern hiring, it is helpful in understanding and evaluating the candidates’ responses during online assessments or job interviews. It is particularly helpful for analyzing the content of their responses, identifying key phrases, and evaluating aspects like clarity, making the process more efficient and data-driven.
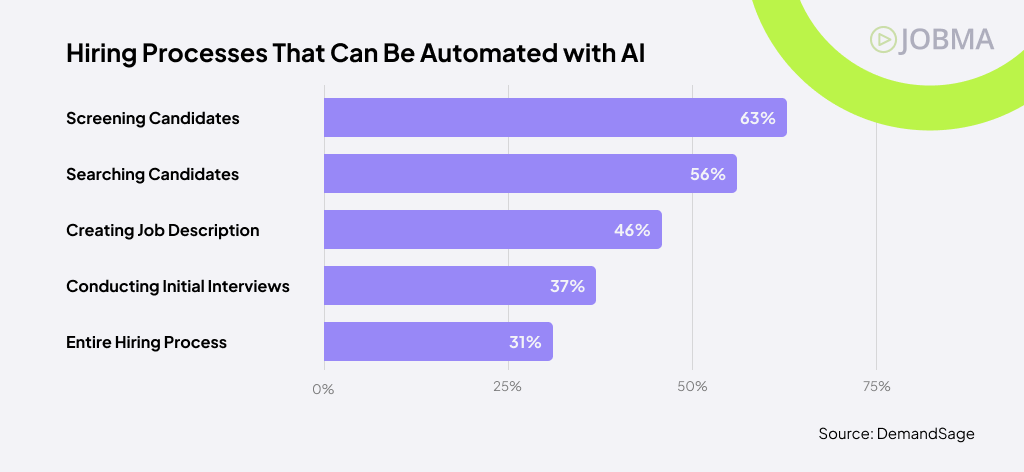
These technologies are not only accelerating adoptions but also continuously evolving. It’s no surprise that many believe AI can replace some parts of the hiring process. A survey report found that respondents believed AI could eventually:
- Screen candidates (63%)
- Search for applicants (56%)
- Generate job descriptions (46%)
- Conduct job interviews (37%)
- Manage the entire recruitment process (31%)
Anna Zhang, Head of Marketing at U7BUY, offers a different perspective. She believes that AI won’t necessarily replace human jobs but rather assist them. In recruitment, she claims that “AI technology will make the whole process a lot easier, faster, and better by allowing recruiters and hiring professionals to get the best talent.”
Zhang continues, “AI won’t replace human recruiters – it will empower them. By automating routine tasks and improving decision-making, AI helps hiring teams focus on what really matters: finding the right talent efficiently and fairly.”
Here are some of the common use cases of AI in recruitment:
- Application Screening: AI tools can assist with resume filtering and even background checks, helping recruiters flag potential issues and focus on qualified applicants.
- Online Assessments: AI can deliver skill-based tests and automatically score results. It streamlines the process, making it faster, more consistent, and scalable across various roles.
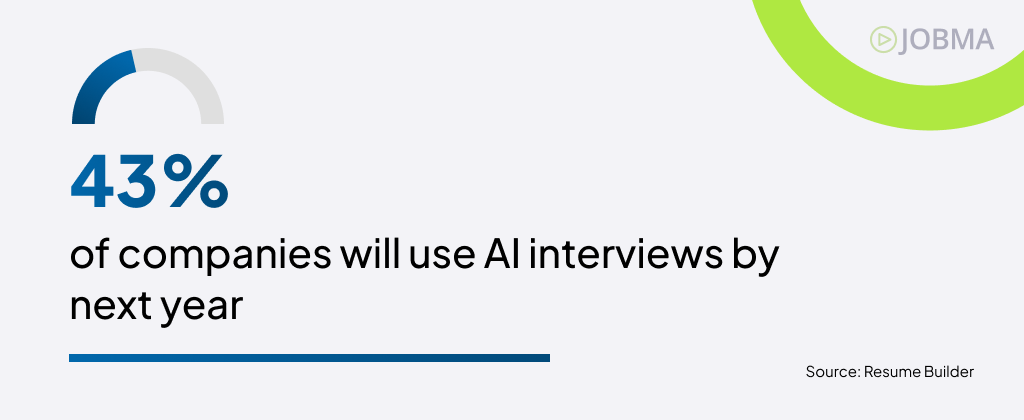
- Virtual Interviews: Nearly 45% of employers will use AI for job interviews, to analyze candidate speech and response quality during video interviews.
- Evaluation: Recruiters are exploring the use of AI to support final hiring decisions by applying data-driven scoring to assess performance. However, these tools are far from perfect, and human oversight remains crucial to ensure fairness and context. Integrating tools like an AI essay humanizer helps maintain the right balance between automation and human tone, especially when generating candidate assessments or communication templates.
Ethical Challenges in AI Recruitment
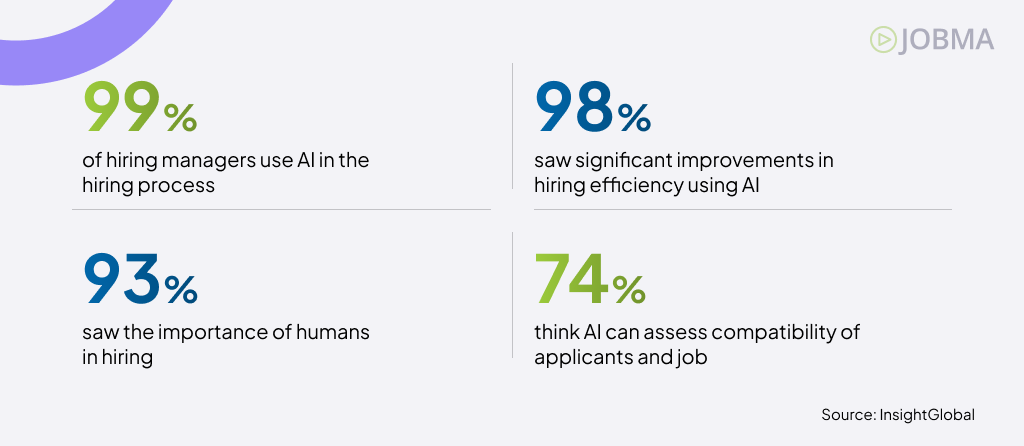
There’s no denying the impact of AI on hiring processes and decision-making. About 98% of recruiters say AI jobs has improved efficiency. Nearly 75% believe it helps match candidates to open roles more accurately. Still, 93% agree that human oversight remains essential in the hiring process.
However, if not implemented thoughtfully, it can lead to serious social, legal, and reputational issues. Beyond damaging your employer’s brand or attracting candidate complaints, it can also trigger regulatory consequences. So, the big question remains: Can AI truly be fair?
Here are the key ethical challenges to keep in mind when implementing AI:
- Biased Hiring Data: AI trained on hiring biased historical data may perpetuate unfair patterns, such as favoring certain schools, genders, or backgrounds. This could lead to repeated, unintentional discrimination.
- Discrimination Risk: Even seemingly neutral data, such as ZIP codes or university affiliations, can serve as indirect indicators of race, gender, or income level. This makes it easy for bias to slip through unnoticed.
- Lack of Transparency: Some AI tools work like black boxes, offering little to no insight into how hiring decisions are made. This makes it difficult for recruiters or candidates to understand or explain how decisions are made.
- Privacy and Security Issues: AI tools often rely on large amounts of candidate data. Without proper safeguards, this could raise concerns about data privacy, consent, and cybersecurity. Partnering with trusted outsourced IT support can help organizations implement strong security frameworks such as synthetic monitoring implementation and ensure compliance with evolving data protection standards
Lacey Jarvis, COO at AAA State of Play, recommends being highly critical of the datasets collected for AI recruitment. She underscores the importance of human oversight in the hiring process to avoid bias and discrimination.
Jarvis explains, “You have to be highly critical of the datasets used in AI recruitment. Why? Because if the input is biased, the output will be too. That’s why human oversight is still key to making sure decisions stay fair and inclusive.”
Meanwhile, Adrian Lorga, Founder & President at 617 Boston Movers, suggests ensuring transparency and accountability in AI hiring practices.
Lorga shares, “Transparency and accountability should be non-negotiables when using AI in hiring. Candidates deserve to know how decisions are made and who’s responsible if something goes wrong.”
Learn how to build a framework for the ethical use of AI in hiring below.

Building a Framework for the Ethical Use of AI in Recruitment
AI promises greater efficiency, better-quality hires, and measurable cost savings. As its adoption accelerates, fairness must remain a non-negotiable priority. This entails ensuring the following:
- Equal Access: Job opportunities must be accessible to all qualified candidates.
- Equitable Opportunity: Providing accommodations to those job applicants in need, like persons with disability (PWD).
- Bias Mitigation: Actively identify and reduce the potential for bias at every stage of the hiring process.
Here’s a three-part framework for the ethical use of AI in recruitment:
1. AI Design and Development: Build with Ethics in Mind From the Get-Go
The first step is to pick AI tools from a reliable service provider. Ethical hiring doesn’t start with audits – it starts with intentional system design. Here’s how to lay the foundation:
- Set Clear, Fair Hiring Goals: Start with clear hiring goals that prioritize fairness, compliance standards, and job-related criteria. This keeps your AI tools aligned with ethical and business objectives.
- Choose Trusted, Transparent AI Tools: Go for AI business solutions and tools like the AI Ad Generator that offer transparency and clear insights into how decisions are made.
- Leverage Bias-Tested Datasets: Regularly review training data to remove hidden patterns. The more balanced your data, the fairer and more accurate your hiring outcomes will be.
- Involve a Cross-Functional Team: Bring in a mix of experts (from HR and legal to tech) to guide the process. This ensures you’re building systems that are not only functional but also fair and compliant.
- Tests Before Launching: Before using AI in real-world hiring scenarios, run bias audits, simulation rounds, and scenario testing to catch red flags early and fine-tune performance.
Leigh McKenzie, Community Advocate at Traffic Think Tank, emphasizes the need for ethics in AI use. She underscores the importance of fair screening to attract and hire the best talent.
McKenzie says, “Ethical AI design isn’t optional but foundational. Fair screening builds trust and helps you hire the right people from the start. If you don’t lead with ethics, you risk undermining both candidate experience and long-term business outcomes.”
2. AI Deployment and Implementation: Use AI Transparently and Responsibly
The next step is to integrate the actual AI with your recruitment systems. Once everything has been properly set in place, you can now kickstart your AI hiring process. However, when it comes to leveraging AI, transparency and responsibility are crucial. Here’s what you need to do:
- Inform the Candidates About the Use of AI: Let candidates know when and how AI is being used during the hiring process. This builds transparency and sets clear expectations from the start.
- Keep Humans in the Loop for Key Decisions: Let AI assist the process, not replace human decision-making. The final decisions should involve human judgment to prevent errors, bias, and missed context. This can be achieved by leveraging AI humanizer tools that enhance the decision-making process without replacing human judgment.
- Document Processes and Decisions Clearly: HR professionals and recruitment teams looking to deepen their understanding of responsible AI implementation can explore structured learning programs like Coursiv, which offers courses on AI ethics, bias mitigation strategies, algorithmic fairness, and compliance frameworks specifically designed for talent acquisition contexts. Clear documentation supports accountability and compliance.
- Define When Humans vs. AI Makes the Call: Set clear boundaries around what AI handles and what stays human-led. This helps avoid confusion and ensures ethical decision-making at every stage. At the same time, conducting regular ai bot testing can highlight areas where human oversight is still needed.
Ian Gardner, Director of Sales and Business Development at Sigma Tax Pro, highlights the value of transparency and accountability for the ethical use of AI. He believes that while it takes responsibility to use AI for recruitment, it demands transparency from the job market.
Gardner explains, “AI can be a powerful tool in recruitment, but only when used with full transparency and accountability. Candidates have a right to know how decisions are made, and companies have a duty to ensure those decisions are fair, ethical, and explainable.”
3. AI Monitoring and Optimization: Monitor, Improve, and Stay Accountable
The final step is to regularly track and enhance your AI tools or platforms, a process made easier with custom AI development services. Ethical AI use doesn’t stop at deployment – it requires ongoing attention. That means monitoring performance, running audits, and making necessary updates to keep everything fair, accurate, and compliant. Here’s how:
- Track Outcome Regularly: Keep an eye on how your AI tools are performing, especially in terms of accuracy, fairness, and outcomes.
- Test and Update Systems Constantly: AI models can drift or become outdated over time. To keep the system reliable and relevant, run performance checks and update it with real-world data. In this context, using AI for Cybersecurity Content helps ensure that protective measures remain effective against evolving threats.
- Establish a Feedback Loop in Place: Create a way for recruiters and candidates to share feedback on their experience. This helps improve the process and builds trust with users.
- Allow Third-Party Reviews: Bring in external experts to audit your AI tools for fairness, bias, and compliance. Independent reviews add credibility and accountability.
- Make Continuous Improvements: Use insights from your audits, testing, and feedback to refine your system and policy. Ethical AI is never a one-and-done – it’s an ongoing process.
Learn from Kathryn MacDonell, CEO at Trilby Misso Lawyers, who witnesses how AI is continually evolving and transforming. She recommends prioritizing the ethical and legal aspects of AI use in hiring or recruitment.
MacDonell suggests, “AI is constantly evolving, which means your oversight must evolve with it. Regular audits, legal checks, and ethical reviews aren’t just best practices. They’re essential to protect both candidates and your organization.”
Final Words
AI has become a powerful ally in the hiring process, helping teams work faster, make smarter decisions, and access a broader pool of talent. But as we lean into automation and predictive tools, we can’t afford to lose sight of the human element.
Efficiency shouldn’t come at the cost of fairness. Building ethical hiring systems means staying grounded in transparency and accountability.

Disclaimer: This article was authored by a guest contributor or third party. The views expressed are their own and do not necessarily reflect those of Jobma. Jobma does not endorse any products, services, or claims mentioned. This content is for informational purposes only.